THCA vs THC: Understanding the Key Differences
- 57 Views
- arslanchaudhary7439@gmail.com
- July 1, 2025
- Blog
Cannabis is a complex plant that contains a wide range of cannabinoids, each with its own unique effects and potential benefits. Among the most well-known cannabinoids are tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). While both compounds are closely related, they have distinct differences in terms of chemical structure, effects, and therapeutic uses.
If you’re curious about the difference between THCA and THC, you’re not alone. Whether you’re a seasoned cannabis enthusiast or just beginning to explore the world of weed, understanding the distinction between these two cannabinoids can enhance your experience. This article will explore THCA vs THC in detail, with a focus on their effects, uses, and the science behind them.
At Weed Delivery Halifax, we aim to provide you with the best cannabis products, including Pre Rolls and Cheap Oz, so you can make informed decisions about your cannabis consumption.
What is THCA?
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is a naturally occurring cannabinoid found in raw cannabis plants. It is the precursor to THC, meaning it is the inactive form of the compound. When cannabis is heated through methods such as smoking, vaping, or cooking, THCA undergoes a process called decarboxylation. During this process, THCA loses a carboxyl group (COOH) and becomes the psychoactive compound THC.
Key Characteristics of THCA:
- Non-Psychoactive: THCA itself does not produce the “high” commonly associated with cannabis use.
- Therapeutic Potential: THCA has been studied for its potential anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-nausea effects.
- Raw Cannabis: You will find THCA in fresh cannabis flowers, leaves, and stems that have not been exposed to heat.
What is THC?
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the most well-known and researched cannabinoid in cannabis. Unlike THCA, THC is the psychoactive compound responsible for the “high” that people experience when consuming cannabis. THC binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, leading to various physical and mental effects.
Key Characteristics of THC:
- Psychoactive: THC is the compound responsible for the euphoric and mind-altering effects of cannabis.
- Therapeutic Effects: THC has been researched for its potential to reduce pain, anxiety, and muscle spasticity, making it a key component in many medicinal cannabis products.
- Decarboxylation: THC is created when THCA undergoes decarboxylation due to heat.
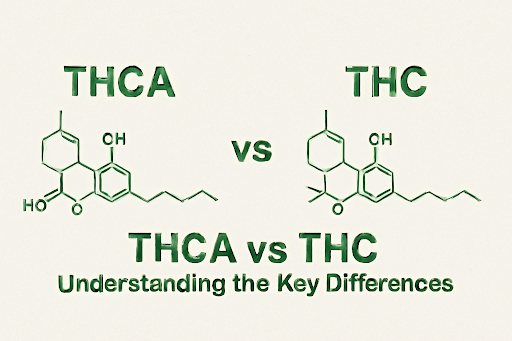
While both THCA and THC are derived from the same cannabis plant, they differ in their molecular structure. THCA has an extra carboxyl group (COOH) that prevents it from binding to cannabinoid receptors in the body. This is why THCA is non-psychoactive, whereas THC, with its extra structure removed, is able to interact with the receptors in the brain to produce the well-known effects.
Key Differences Between THCA and THC:
- Chemical Structure: THCA contains a carboxyl group (COOH), while THC has no carboxyl group. This structural difference is essential in determining the psychoactive properties of these compounds.
- Psychoactive Effects: THCA is non-psychoactive, meaning it does not produce the “high” associated with cannabis consumption. On the other hand, THC is psychoactive and is responsible for the euphoric and mind-altering effects commonly experienced by cannabis users.
- Therapeutic Benefits: THCA is mainly known for its potential anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, which are beneficial for conditions like arthritis or neurodegenerative diseases. THC, however, is widely researched for its pain-relieving, anti-anxiety, and anti-nausea properties, making it a popular choice for medical cannabis use.
- Decarboxylation: THCA is found in its raw form in the cannabis plant and is not decarboxylated, meaning it has not undergone the heating process that would activate its psychoactive effects. THC, however, is the result of THCA being decarboxylated (usually through heating), which removes the carboxyl group and activates its psychoactive properties.
Effects and Benefits: THCA vs THC
THCA Effects:
Since THCA is non-psychoactive, it does not cause the typical “high” that many cannabis users are familiar with. However, research suggests that THCA has several potential benefits, especially in the raw form of cannabis.
- Anti-Inflammatory: THCA has shown promise as a potent anti-inflammatory compound, making it useful for individuals with chronic conditions like arthritis or autoimmune diseases.
- Neuroprotective: Some studies have suggested that THCA may help protect brain cells and potentially aid in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
- Anti-Nausea: THCA may help reduce nausea and vomiting, which could benefit those undergoing chemotherapy or dealing with digestive issues.
THC Effects:
THC is the compound responsible for the psychoactive effects that cannabis is known for. It produces a range of effects depending on the strain and dosage, including euphoria, relaxation, and heightened sensory perception.
- Pain Relief: THC is often used in medical cannabis for its analgesic properties, helping to alleviate chronic pain and muscle spasms.
- Mood Elevation: Many users report feeling uplifted, relaxed, and euphoric after consuming THC, which is why it is commonly used for recreational purposes.
- Appetite Stimulation: THC is known for increasing appetite, often referred to as the “munchies,” which can help patients undergoing treatments like chemotherapy that cause a loss of appetite.
How to Consume THCA and THC
There are various ways to consume both THCA and THC, depending on whether the cannabis is raw or decarboxylated. Here’s how each compound is typically consumed:
THCA Consumption:
- Raw Cannabis: THCA is found in the raw cannabis plant, so consuming fresh cannabis flowers, leaves, or juicing raw cannabis can provide THCA without any psychoactive effects.
- THCA Oil and Tinctures: Some companies offer THCA oil or tinctures that can be consumed sublingually for potential health benefits without getting high.
THC Consumption:
- Smoking/Vaping: Smoking or vaping cannabis is one of the most popular methods for consuming THC. When heated, THCA decarboxylates into THC, producing the desired psychoactive effects.
- Edibles: THC is commonly consumed in the form of edibles like gummies, brownies, or capsules. These products provide a longer-lasting high compared to smoking or vaping.
- Concentrates: THC concentrates, such as shatter, wax, or oils, offer a potent dose of THC and are commonly used by experienced cannabis consumers.
Pre Rolls and Cheap Oz: A Quick Introduction
At Weed Delivery Halifax, we offer a variety of cannabis products that cater to different preferences. If you’re looking for a convenient, ready-to-smoke option, try our Pre Rolls. For those looking to stock up, we also offer Cheap Oz with great deals for bulk purchases. These products often contain THC, providing the well-known effects that recreational users love.
Conclusion
In summary, while THCA and THC are closely related, they serve very different purposes. THCA, the raw, non-psychoactive form of THC, is believed to have various health benefits, particularly in the realms of anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. On the other hand, THC is the compound that produces the well-known “high” and is commonly used for pain relief, mood elevation, and appetite stimulation.
Understanding the distinction between THCA and THC allows consumers to make informed choices about their cannabis use, whether they are seeking therapeutic benefits or recreational effects. At Weed Delivery Halifax, we provide a wide range of cannabis products, including Pre Rolls and Cheap Oz, to meet your individual needs.
By choosing the right products and methods of consumption, you can tailor your cannabis experience to suit your health goals or recreational preferences.
For more visit study cafe.